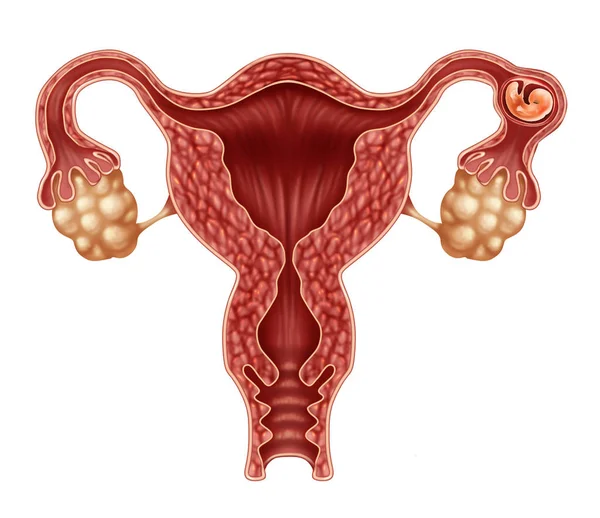
Extra uterine pregnancy, also known as ectopic pregnancy, is an obstetric complication in which the fertilised egg implants outside the uterine cavity. It occurs in around 2% of pregnancies and can have major repercussions on the health of the woman concerned.
An extra uterine pregnancy occurs when the fertilised egg fails to reach the uterine cavity to implant in the endometrial wall. Instead, it usually implants in the fallopian tubes. The term “extrauterine” literally means “outside the uterus”.
Several factors can hinder the passage of the ovum to the uterus, resulting in an ectopic pregnancy:
Early diagnosis is crucial to avoid serious complications. Here are some common symptoms:
Abnormal vaginal bleeding, often irregular and light, can be a warning sign. Although it can sometimes be mistaken for menstruation, it should raise a red flag.
Sudden, intense, localised pain in the pelvic area is common and often indicates that the fertilised egg has implanted outside the uterine cavity.
Other signs may include shoulder pain (due to irritation of the diaphragm caused by internal bleeding), dizziness or fainting, indicating the presence of a medical emergency.
Diagnosis often begins with a clinical examination, followed by blood tests to measure levels of pregnancy hormone (hCG). A transvaginal ultrasound scan then confirms whether or not the pregnancy is located in the uterus.
When diagnosed early, it can be treated with medication. Methotrexate is commonly used to stop the growth of embryonic tissue.
If the fallopian tubes rupture or there is significant haemorrhage, surgery becomes necessary. Laparoscopic surgery involves inserting surgical instruments through small incisions to remove the implanted embryo and repair or remove the damaged tube.
If left untreated, it can lead to complications, mainly due to tubal rupture.
When the fertilised egg grows in a fallopian tube without treatment, the tube may rupture, causing serious internal haemorrhage requiring emergency intervention.
Women who have experienced this type of pregnancy may find it difficult to conceive again. The likelihood of future ectopic pregnancies also increases after a first experience.
Although there is no infallible method for preventing an ectopic pregnancy, certain measures can reduce the risks.
Regular use of protection during sex reduces the risk of sexually transmitted infections such as chlamydia and gonorrhoea, which can damage the fallopian tubes.
Women with a history of extra uterine pregnancy or problems with the fallopian tubes should keep a close eye on early symptoms in the event of a new pregnancy.
